As part of the “STECCI” project, a team from Heritage Malta, along with representatives from the University of Donja Gorica, conducted an important field activity in Zabljak from August 6 to 10, 2024. This activity was part of Task 4.1 under Work Package 4 (WP 4) of the project, which aims to digitize cultural heritage using advanced technological methods. This significant milestone furthers our mission to protect Europe’s cultural treasures through innovative, sustainable strategies.
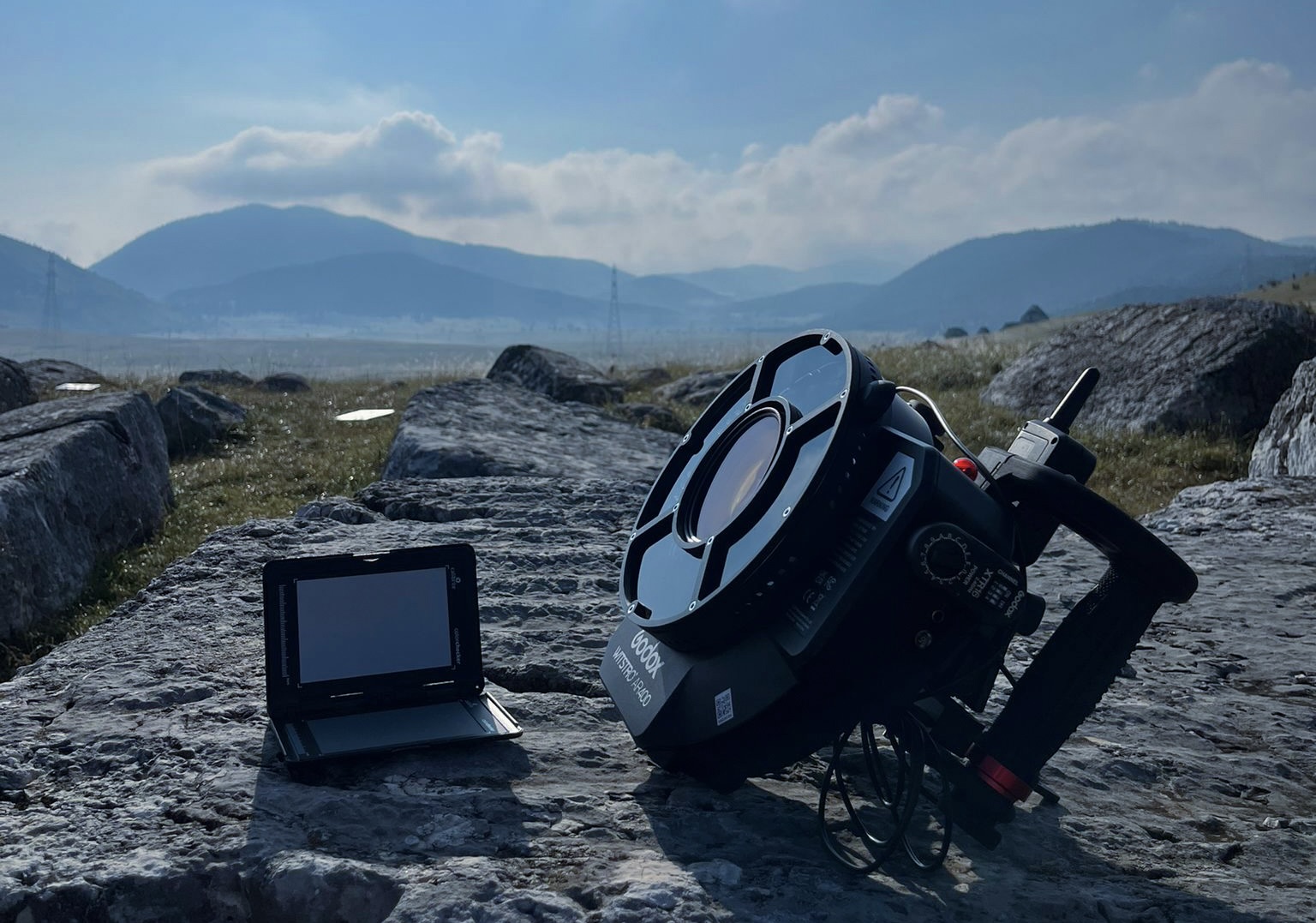
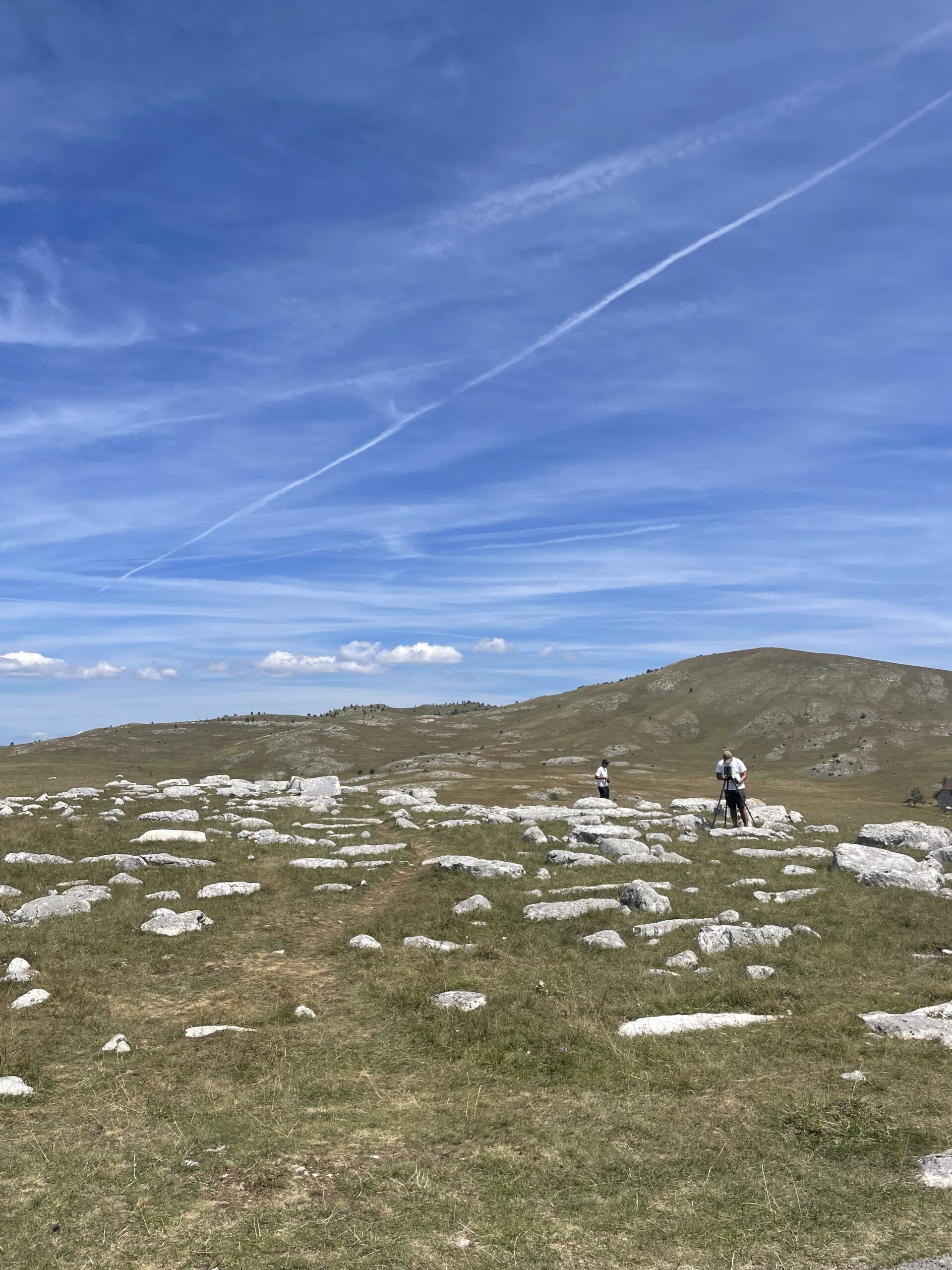
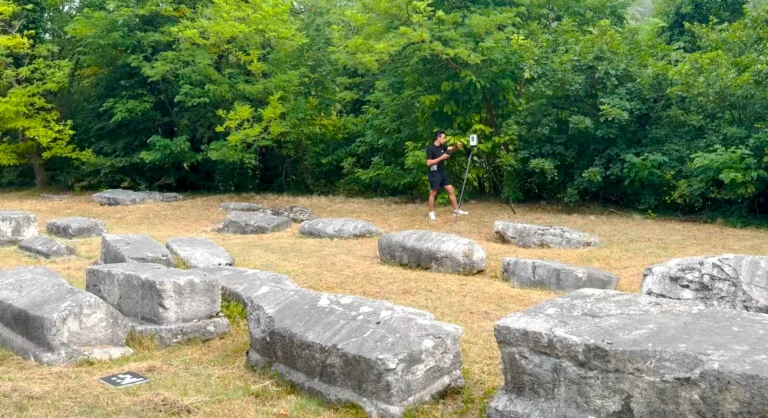
The team from Heritage Malta, consisting of Jacob Saliba, Francesco Vello, and Aaron Cole, along with Aleksandra Gogic and Vedran Pean from the University of Donja Gorica, employed advanced digitalization methods to create precise and high-quality digital models of the sites and artifacts, such as aerial scanning with drones, photogrammetry, and LiDAR, Heritage Malta captured highly accurate 3D models of the Stećci tombstones. This data collection is a critical step in STECCI project, as it enables us to create detailed digital replicas that can be used for research, conservation, and public engagement.
Key Objectives Achieved:
• Comprehensive Data Collection: We successfully documented the Stećci using a combination of advanced digitization technologies.
• Evaluation of Methods: Our team evaluated the accuracy, ease of use, and sustainability of various digital acquisition methods.
• Creation of 3D Models: The data collected will be used to develop high-quality 3D models, supporting future conservation efforts and educational initiatives.
The digital models created during this acquisition will be integrated into the broader framework of the project. These models will be made publicly accessible online, promoting awareness and education around the importance of preserving cultural heritage.
Note: Task 4.1 under Work Package 4 (WP 4) encompasses the following key activities:
- Aerial Photogrammetry: This technique was used to create a georeferenced 3D model of the entire site. Aerial photogrammetry allows for detailed aerial imaging of the terrain, providing an accurate representation of the site and enabling a better understanding of its characteristics. This 3D model will serve as a foundation for further analysis and research, allowing individual artifacts to be used as reference points.
- 3D Scanning of Artifacts: Within this activity, the team used various 3D scanning methods, including photogrammetry and LiDAR technology, to meticulously document the artifacts at each site. This method enables the creation of highly accurate digital replicas of the artifacts, which will be available for further research and analysis. Additionally, developing a predefined methodology for selecting and scanning artifacts is one of the important outcomes of the project.